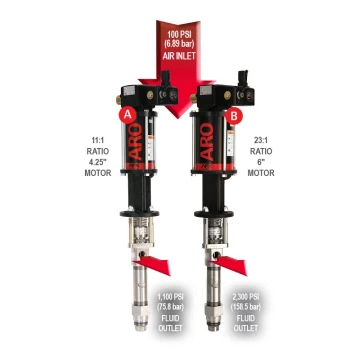
How do air operated piston pumps work?
Air operated piston pump technology works by utilizing compressed air to generate force and move a piston within a cylinder. As air is supplied to one side of the piston, it creates pressure, causing the piston to move and draw in fluid through an inlet valve. When the air is released and supplied to the other side of the piston, it pushes the fluid out through an outlet valve, enabling the pump to transfer fluids effectively.
Piston pumps are used in a wide variety of fluid handling applications. The majority of these can be broken down into four different categories: